In the land of endless summer, where the sun perpetually shines, and the Pacific Ocean kisses the coastline, there’s a unique thrill that comes with riding a motorcycle in California.
From the scenic beauty of Highway 1, weaving along the coast through Big Sur, to the arid allure of Death Valley’s desert landscapes, the Golden State offers a smorgasbord of visual delights that make every ride a memorable adventure.
The year-round favorable weather is just the cherry on top, transforming motorcycle riding from a convenient mode of transportation into an exhilarating lifestyle for weekend warriors.
But as intoxicating as the call of the open road may be, every rider — whether a local Californian or a visitor — must understand and adhere to California’s motorcycle laws.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to navigating these safety laws, ensuring every ride you take under the Californian sun isn’t just thrilling but also safe and within the rules of the road. Plus, you’ll know what to do if an unfortunate motorcycle accident happens.
Acquiring a Motorcycle License in California
Motorcycle accidents happen often, especially in the state of California. Understanding the following procedures and requirements is the first step toward getting a California motorcycle license.
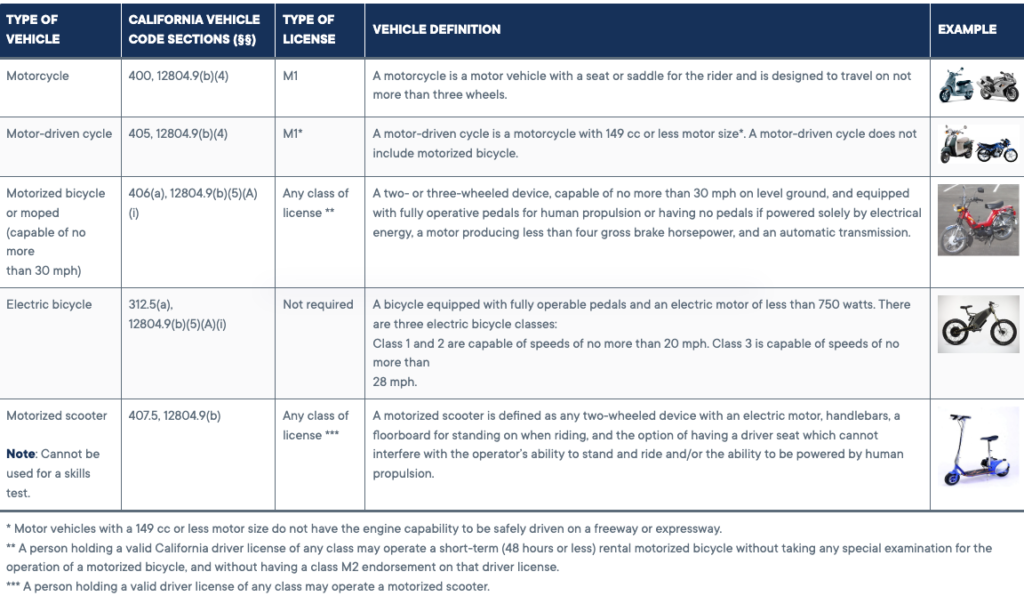
Types of Motorcycle Licenses
California offers two DL classes for two-wheel vehicle operation: Class M1 and Class M2.
The M1 license allows you to operate any two-wheel motorcycle, motor-driven cycle, or motorized scooter and all vehicles under Class M2.
The M2 license restricts you to only motorized bicycles, mopeds, or motorized scooters.
Additionally, Class C licensees may operate a motorcycle with a sidecar attached, a three-wheel motorcycle, or a motorized scooter.
Source: California Department of Motor Vehicle (DMV)
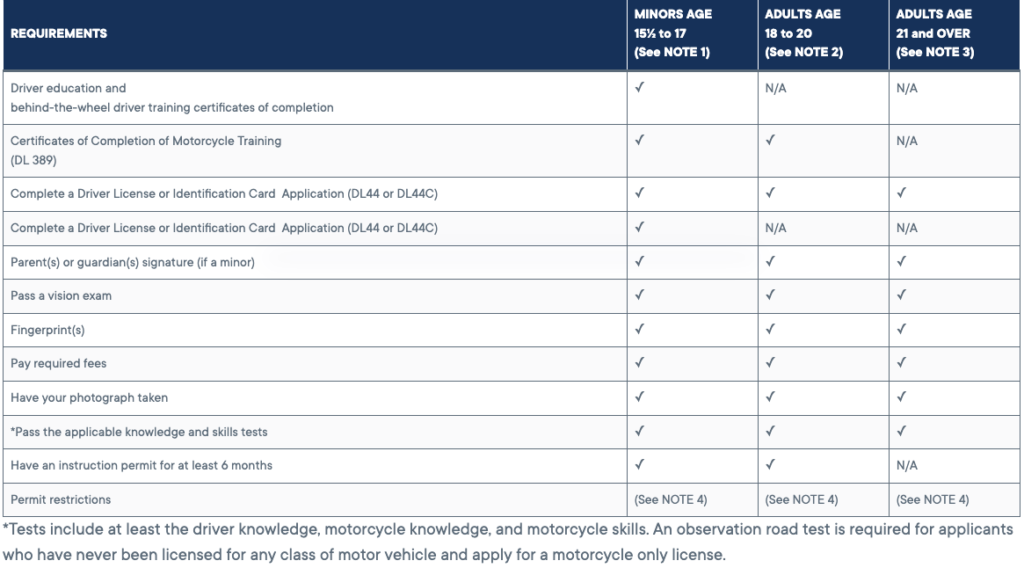
Eligibility Criteria
You must be at least 15 and a half years old. If you are under 18, you must have a driver’s education and behind-the-wheel driver training certificates of completion, as well as complete a learner’s permit in the form of a Driver’s License or Identification Card Application (DL44 or DL44C).
Anyone under 21 must have the following:
- Certificates of Completion of Motorcycle Training (DL 389)
- An instruction permit for at least six months
All applicants must:
- Complete a Driver’s License or Identification Card Application (DL44 or DL44C)
- Provide a parent(s) or guardian(s) signature (if a minor)
- Pass a vision exam
- Provide fingerprint(s)
- Pay required fees
- Have a photograph taken
- Pass the applicable knowledge and skills test. Tests include at least the driver knowledge, motorcycle knowledge, and motorcycle skills. An observation road test is required for applicants who have never been licensed for any class of motor vehicle and are applying for a motorcycle-only license.
Source: California Department of Motor Vehicle (DMV)
The California Motorcycle Safety Program (CMSP)
This program is a prerequisite for young riders, specifically those under 21, before receiving a motorcycle instruction permit.
The CMSP provides comprehensive training among beginner and experienced motorcycle riders, covering all aspects of safe motorcycle operation, including effective turning, braking, and obstacle avoidance techniques.
Upon completing the CMSP training course and submitting the Certificate of Completion of Motorcycle Training (DL 389), you may be exempted from the DMV motorcycle skills test.
The DMV does not exempt the motorcycle skills test even if you have completed an out-of-state motorcycle training program or possess an in-state/out-of-state course completion card for insurance purposes.
Completion of this course not only increases your safety on the road but also satisfies the training requirements for a Class M1 or M2 license.
Because of this, CMSP is encouraged among motorcycle applicants aged 21 years and older.
Testing Requirements
After meeting the initial eligibility criteria and completing the CMSP course, the next step involves passing a series of tests.
To acquire your desired license class(es) in California, you must complete several knowledge tests, including the driver knowledge test, motorcycle knowledge test, and any additional tests relevant to your chosen license class(es).
You must pass a motorcycle skills test or obtain a Certificate of Completion of Motorcycle Training (DL 389) as outlined in the California Motorcyclist Safety Program Training Course section. DL 389 only remains valid for 12 months from the date of issue.
Note that when applying for a motorcycle-only (Class M1/M2) license, you may still be required to undergo an observation test.
Penalties for Riding Without a Motorcycle License
Riding a motorcycle without the appropriate license is not only illegal but also risky. It can result in considerable penalties that vary based on jurisdiction and circumstances. Here are some of the potential consequences you might face.
Fines and Monetary Consequences
Fines for riding a motorcycle without a license can range broadly from $250 to $1,000. The exact amount often depends on the discretion of the arresting officer and the specific circumstances of the violation. It can be charged either as a misdemeanor or an infraction.
Potential Jail Time or Community Service
For misdemeanors, individuals may face up to six months of jail time and a court fine of $1,000.
If an infraction occurs, the damage is a maximum of $250 court fine.
Prosecutors may be willing to downgrade a charge of California Vehicle Code Section 12500 VC to an infraction or even dismiss the case if the defendant obtains a valid California driver’s license while the charges are pending.
Impounding of Motorcycle
In many cases, if you’re caught riding without a license, your motorcycle can be impounded. This means you’ll not only have to pay fines but also the costs associated with retrieving your vehicle from the impound lot.
The standard impound fee in the state of California is $136.50. The daily storage rates at the official police garages (OPGs) can add up quickly. Motorcycle storage costs $11.50 daily, subject to a 10% city parking occupancy tax.
Additional charges may apply, such as a mileage rate of $7.50, particularly if the towing operator needs to travel a long distance to collect and transport the vehicle. Plus, an additional fee of $77.00 if the police had to remove any stolen parts from the car.
And if you want the city to return the motorcycle, you’ll have to pay a release fee of $115.
If you fail to pay these fees, a lien will be placed on the title of your vehicle. The city will then proceed with a lien sale to recover the outstanding fees owed.
Impact on Insurance Rates and Coverage
Being caught without a motorcycle license can seriously affect your insurance rates. It could lead to higher premiums or even denial of coverage.
Moreover, if you cause an accident while riding unlicensed, your insurance might not cover the damages, leaving you financially responsible.
Future Implications for Licensing and Record
Getting caught without a license can have long-term effects on your driving record. It could make obtaining a legitimate license more difficult in the future.
In some cases, repeated offenses could result in a suspended license.
Essential Rules for Riding a Motorcycle in California
Riding a motorcycle in California can be an exhilarating experience, but it’s essential to understand and follow the rules and speed limits to ensure overall road safety.
Helmet Laws
Helmets reduced the risk of severe brain and head injuries during a motorcycle crash by a substantial 63%-88% and the upper and mid-face by 65%.
In California, it is illegal for motorists to get on the road without wearing a motorcycle safety helmet that complies with U.S. Department of Transportation or U.S. DOT-approved standards. This also applies to passengers.
Helmets must have a thick inner liner, sturdy chin straps and rivets, a weight of approximately three pounds, and a design free from protruding elements.
Lane Sharing or Splitting
Lane splitting, the practice of riding between lanes of traffic, is legal in California. However, motorcycle drivers should only lane split when it is safe, considering factors such as speed, traffic conditions, weather, blind spots, and road surface.
Safety Equipment Requirements
Motorcycles in California must be equipped with right and left mirrors. They must also have functioning turn signals, brakes, and a horn. Headlights and taillights must be on at all times, even during daylight hours.
Passenger Restrictions
If a motorcycle is carrying a passenger, it must have separate footrests for the passenger. The passenger must also wear a helmet that complies with the same safety standards applicable to riders.
Noise Limitations and Muffler Requirements
California law requires motorcycles to have a muffler to prevent excessive noise and disruptive emissions. There are specific sound level limits based on the year of manufacture and speed of the motorcycle.
DUI Laws and Penalties Specific to Motorcyclists
If a motorcyclist 21 years old and up is found to have a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.08% or higher, they can be charged with a DUI.
If they’re under 21 years old, BAC should NOT reach 0.01%.
Penalties can include fines, license suspension, mandatory alcohol education programs, and even jail time.
Motorcycle Accidents Can Happen Anywhere—If You’ve Been Involved in a California Motorcycle Accident, Contact Frantz Law Group
Accidents, property damage, and bodily injury can still happen despite our best efforts to ride safely and responsibly. The aftermath can be confusing and stressful.
If you or a loved one have been involved in a motorcycle accident in California, it’s essential to seek legal counsel as soon as possible. The experienced motorcycle accident lawyers at Frantz Law Group are ready to help.
We will guide you through the complexities of the legal process, negotiate with insurance companies, and ensure you understand your rights and options.
Don’t try to navigate this challenging time alone. Contact Frantz Law Group today for a free consultation. We’re here to help you get the justice and compensation you deserve.
Reach out to the motorcycle accident attorneys at our law firm today.
